Introduction, Features, Workflow, and Applications of ChIP-Seq
Introduction of Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Sequencing (ChIP-Seq) ChIP (Chromatin Immunoprecipitation) is the cross-linking of intracellular proteins with DNA under physiological conditions and fixing protein-DNA complexes in the living cell state, cutting them randomly into chromatin fragments of a certain length under the action of ultrasound, then precipitating the complex, specifically enriching the target protein-bound DNA fragments,…
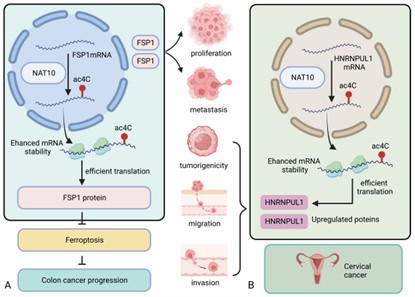
Applications and Discoveries in RNA Acetylation Studies
RNA acetylation modification, as an emerging form of epigenetic regulation, exhibits important functions in regulating gene expression, translation efficiency and RNA stability. In particular, N4-acetylcytosine (ac4C) modification has become a hot spot of research in recent years due to its wide distribution and significant biological effects. With the development of acRIP-seq (acetylated RNA Immunoprecipitation sequencing) technology,…
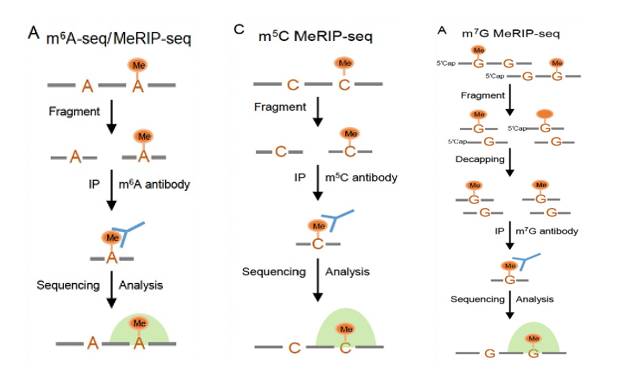
Principle, Protocol, Bioinformatics and Applications in Diseases of MeRIP-seq
Epitranscriptome pertains to the phenomenon wherein gene expression is modulated by chemical alterations on RNA without altering the RNA sequence. There exist over 100 types of intracellular RNA modifications, with the majority being conspicuous modifications on tRNA and other non-coding RNA and only a few modifications on mRNA. The most abundant modification in mRNA is N6-methyladenosine…
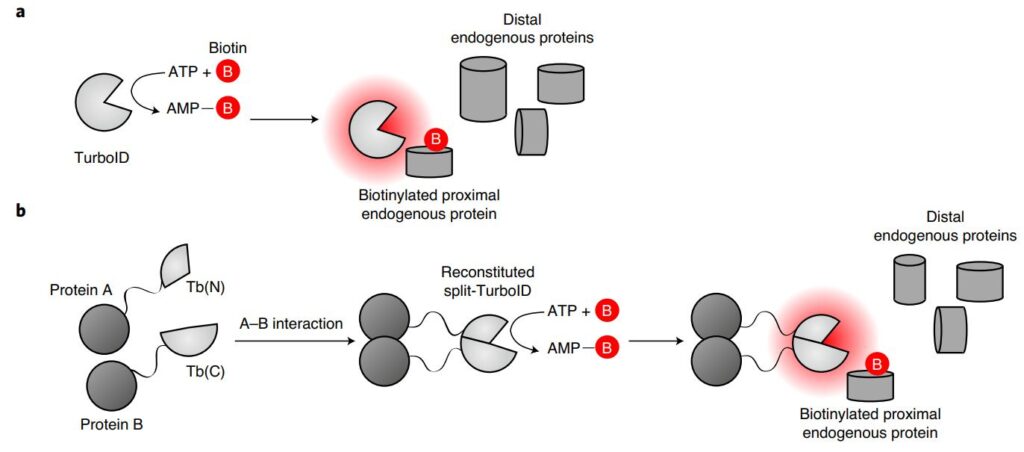
Proximity Labeling Techniques
Proximity labeling works by fusing the decoy protein to be studied with an enzyme that nonspecifically labels the surrounding protein. The tagged proteins are called “prey” proteins. There is a rapid development of protein labeling techniques based on proximity-tagging enzymes. Biotin-dependent biotin identification (BioID) of biotin ligase mutants relying on biotin ligase (BirA), which can label lysine…
DAP-seq: Principles, Workflow and Analysis
Overview of DAP-seq The DNA Affinity Purification Sequencing (DAP-seq) technique is an innovative method aimed at exploring the interactions between transcription factors (TFs) and genomic DNA. By simulating the interaction between TFs and their DNA binding sites in vitro, this technology reveals key DNA sequences in gene regulatory networks. In contrast to traditional Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Sequencing (ChIP-seq), DAP-seq is…
The Applications of DAP-seq Technology
Transcription factors (TFs) binding to specific locations in the genome influence dynamic changes in transcription levels. Disruption of TF binding sites (TFBS) correlates with phenotypic diversity and disease states, including agriculturally important adaptive traits and various diseases like cancer. Characterizing the genome-wide binding spectrum is crucial for exploring these mechanisms. DNA affinity purification sequencing (DAP-seq) is a…
Uncovering RNA-Protein Interactions with RNA Antisense Purification and Mass Spectrometry (RAP-MS)
What is RAP-MS? RNA molecules play a vital role in cellular functions, ranging from gene expression regulation to protein synthesis. Understanding the interactions between RNA and proteins is crucial to comprehend the intricate mechanisms of cellular biology. However, identifying RNA-protein interactions can be challenging, especially for long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) that do not encode proteins. RNA antisense…
ChIRP and ChIRP-Seq Techniques in Studying Gene Expression Regulation
The intricate interplay between DNA and histone proteins results in the formation of chromatin, which performs a pivotal function in governing the expression of genes. The dynamic process of chromatin remodeling and modifications plays a decisive role in regulating the accessibility of DNA to the transcriptional machinery, thereby leaving an indelible imprint on gene expression….